6 Key Facts About Basic Atomic Structure
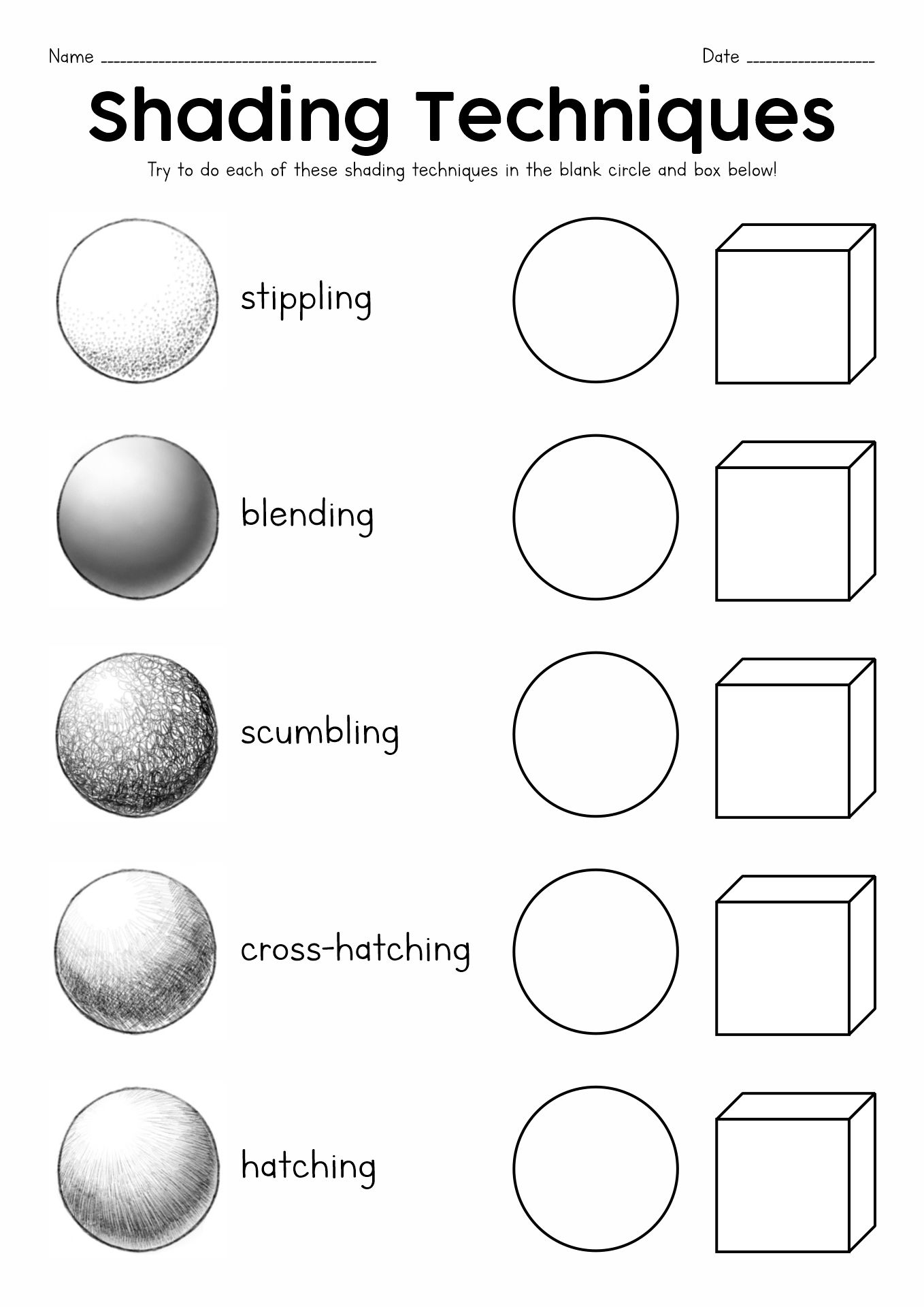
Understanding the Basics of Atomic Structure
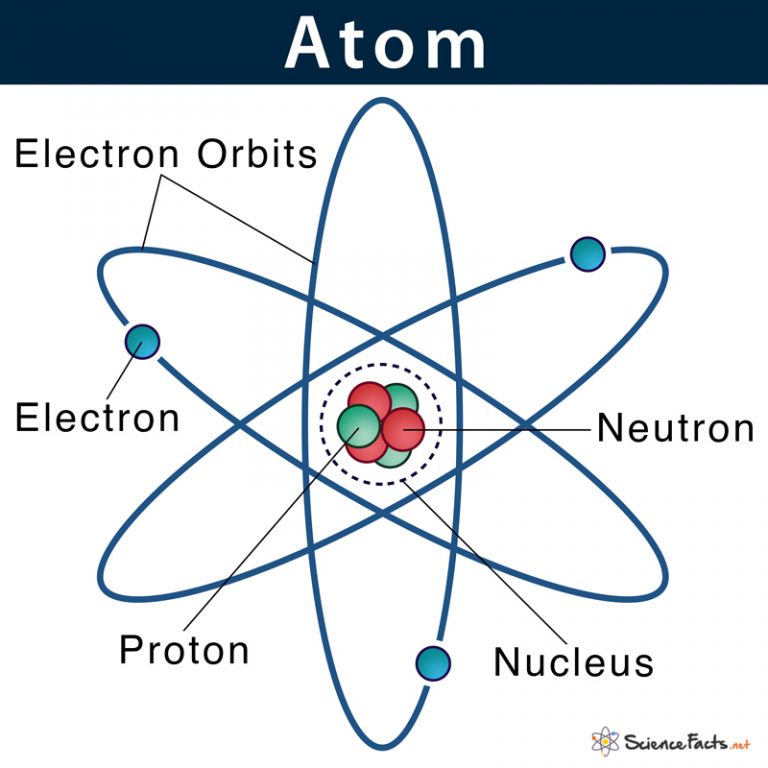
The atomic structure is the foundation of chemistry and physics, and understanding its basic principles is crucial for any student or enthusiast of these sciences. The atomic structure is composed of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of these components plays a vital role in determining the properties of an element. In this article, we will explore six key facts about basic atomic structure that will help you grasp this fundamental concept.
Fact 1: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
The atom is composed of three main particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus, which is the central part of the atom. Neutrons have no charge and are also found in the nucleus. Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
⚠️ Note: The number of protons in an atom is also known as the atomic number.
Fact 2: The Nucleus
The nucleus is the central part of the atom, and it contains the protons and neutrons. The nucleus is extremely small, with a diameter of about 1⁄100,000 the diameter of the atom. Despite its small size, the nucleus contains most of the atom’s mass. The protons and neutrons in the nucleus are held together by the strong nuclear force, which is one of the four fundamental forces of nature.
Fact 3: Electron Shells
Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells. Each energy level can hold a specific number of electrons, and when an energy level is full, electrons begin to occupy the next energy level. The first energy level can hold up to two electrons, while the second energy level can hold up to eight electrons. Electron shells are further divided into subshells, which are designated by the letters s, p, d, and f.
Fact 4: Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its atoms. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. The mass number is also known as the atomic mass. The atomic number determines the element of an atom, while the mass number determines the isotope of an element.

| Atomic Number | Mass Number | Element |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 12 | Carbon |
| 6 | 13 | Carbon |
| 6 | 14 | Carbon |
Fact 5: Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. For example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 are all isotopes of carbon.
Fact 6: Atomic Radius
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron in an atom. The atomic radius increases as you move down a group in the periodic table and decreases as you move across a period. The atomic radius is an important factor in determining the chemical properties of an element.
🔍 Note: The atomic radius is not a fixed value and can vary depending on the source.
In conclusion, understanding the basic atomic structure is crucial for any student or enthusiast of chemistry and physics. By grasping the six key facts outlined in this article, you will have a solid foundation in the basics of atomic structure and be well on your way to exploring more advanced topics in these sciences.
What is the atomic number?
+The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom, which determines the element of an atom.
What is the difference between atomic number and mass number?
+The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom, while the mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
What are isotopes?
+Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.