5 Steps to Balancing Equations Like a Pro
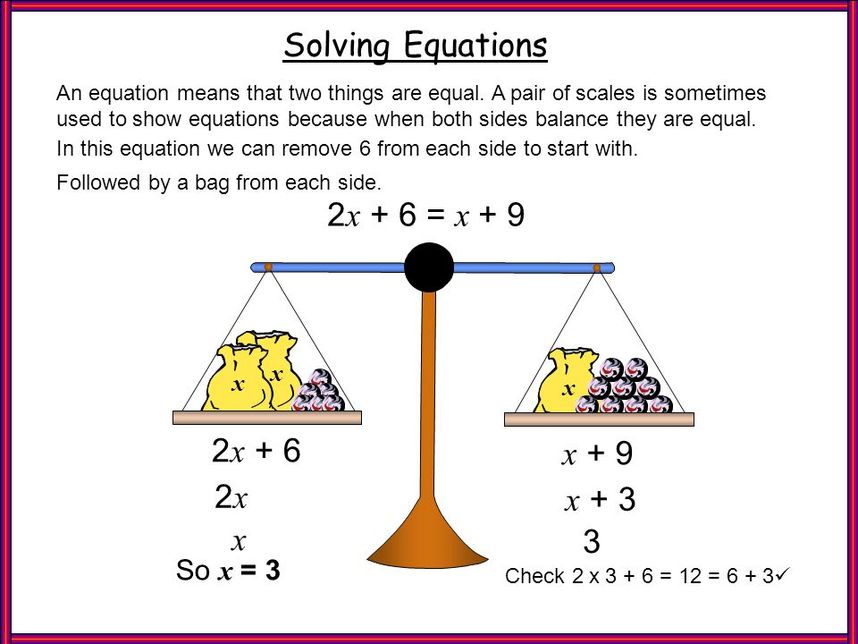
Understanding the Basics of Balancing Equations
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill in chemistry, and it can be a daunting task for many students. However, with practice and patience, anyone can become proficient in balancing equations like a pro. In this article, we will break down the process of balancing equations into five manageable steps.
Step 1: Write Down the Unbalanced Equation
The first step in balancing an equation is to write down the unbalanced equation. This involves writing the reactants on the left side of the equation and the products on the right side. Make sure to include all the reactants and products, and write their chemical formulas correctly.
💡 Note: Always start with the unbalanced equation, as it will help you identify the atoms that need to be balanced.
Step 2: Count the Atoms of Each Element
Once you have written down the unbalanced equation, count the number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides. This will help you identify which elements are not balanced.
- Reactants:
- 2 atoms of hydrogen (H)
- 1 atom of oxygen (O)
- Products:
- 2 atoms of hydrogen (H)
- 1 atom of oxygen (O)
Step 3: Balance the Atoms of Each Element
Now that you have counted the atoms of each element, it’s time to balance them. Start by balancing the elements that appear most frequently in the equation. In this case, we will start with hydrogen (H).
- Add a coefficient of 2 in front of H2O to balance the hydrogen atoms:
- 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Next, balance the oxygen atoms:
- Add a coefficient of 2 in front of O2 to balance the oxygen atoms:
- 2H2 + 2O2 → 2H2O
Step 4: Check Your Work
Once you have balanced the equation, check your work to make sure that each element has the same number of atoms on both the reactant and product sides.
- Reactants:
- 4 atoms of hydrogen (H)
- 4 atoms of oxygen (O)
- Products:
- 4 atoms of hydrogen (H)
- 4 atoms of oxygen (O)
If the numbers of atoms for each element are equal on both sides, then the equation is balanced.
Step 5: Write the Balanced Equation
The final step is to write the balanced equation. Make sure to include all the coefficients and subscripts that you have added during the balancing process.
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Example of a Balanced Equation
Here is an example of a balanced equation:
Na + Cl2 → NaCl
In this equation, sodium (Na) reacts with chlorine gas (Cl2) to form sodium chloride (NaCl). The numbers of atoms for each element are equal on both sides, making this a balanced equation.
| Element | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium (Na) | 1 | 1 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | 2 | 1 |
By following these five steps, you can balance even the most complex chemical equations like a pro.
Balancing equations is an essential skill in chemistry, and it requires practice and patience to master. By following these steps and practicing regularly, you can become proficient in balancing equations and improve your understanding of chemical reactions.
What is the importance of balancing chemical equations?
+Balancing chemical equations is crucial in chemistry as it helps to ensure that the number of atoms for each element is equal on both the reactant and product sides, which is a fundamental principle of chemistry.
How do I know if an equation is balanced?
+An equation is balanced if the number of atoms for each element is equal on both the reactant and product sides.
What is the purpose of coefficients in balancing equations?
+Coefficients are used to balance the number of atoms for each element in an equation. They are numbers placed in front of the formulas of reactants or products to indicate the number of molecules or atoms involved in the reaction.