Atp Adp Energy Cycle Worksheet Answer Key

Atp Adp Energy Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
This answer key is designed to help students and educators understand the ATP-ADP energy cycle, a fundamental concept in biochemistry and cellular biology. The energy cycle is crucial for various cellular processes, including energy transfer and storage.
What is the ATP-ADP Energy Cycle?
The ATP-ADP energy cycle, also known as the ATP-ADP ATPase cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur within cells to generate energy. This cycle involves the conversion of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and the subsequent regeneration of ATP from ADP.
Step-by-Step Explanation of the ATP-ADP Energy Cycle
The ATP-ADP energy cycle consists of two main stages: energy release and energy storage.
Stage 1: Energy Release
- Step 1: Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi
- Reaction: ATP → ADP + Pi (inorganic phosphate)
- Energy release: Energy is released when the phosphate bond in ATP is broken
- Importance: Energy is released to perform various cellular functions, such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and membrane transport
Stage 2: Energy Storage
- Step 2: Phosphorylation of ADP to ATP
- Reaction: ADP + Pi → ATP
- Energy storage: Energy is stored when ADP is phosphorylated to form ATP
- Importance: ATP is regenerated and stored for future energy needs
Key Players in the ATP-ADP Energy Cycle
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): Energy-rich molecule that stores energy in the form of phosphate bonds
- ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate): Energy-poor molecule that is converted to ATP during energy storage
- Pi (Inorganic Phosphate): Inorganic phosphate group that is released during energy release and used during energy storage
Importance of the ATP-ADP Energy Cycle
- Energy Transfer: The ATP-ADP energy cycle allows for efficient energy transfer between different cellular processes
- Energy Storage: The cycle enables cells to store energy for future needs
- Cellular Functions: The energy cycle supports various cellular functions, including muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and membrane transport
📝 Note: The ATP-ADP energy cycle is a continuous process that occurs within cells to generate and store energy.
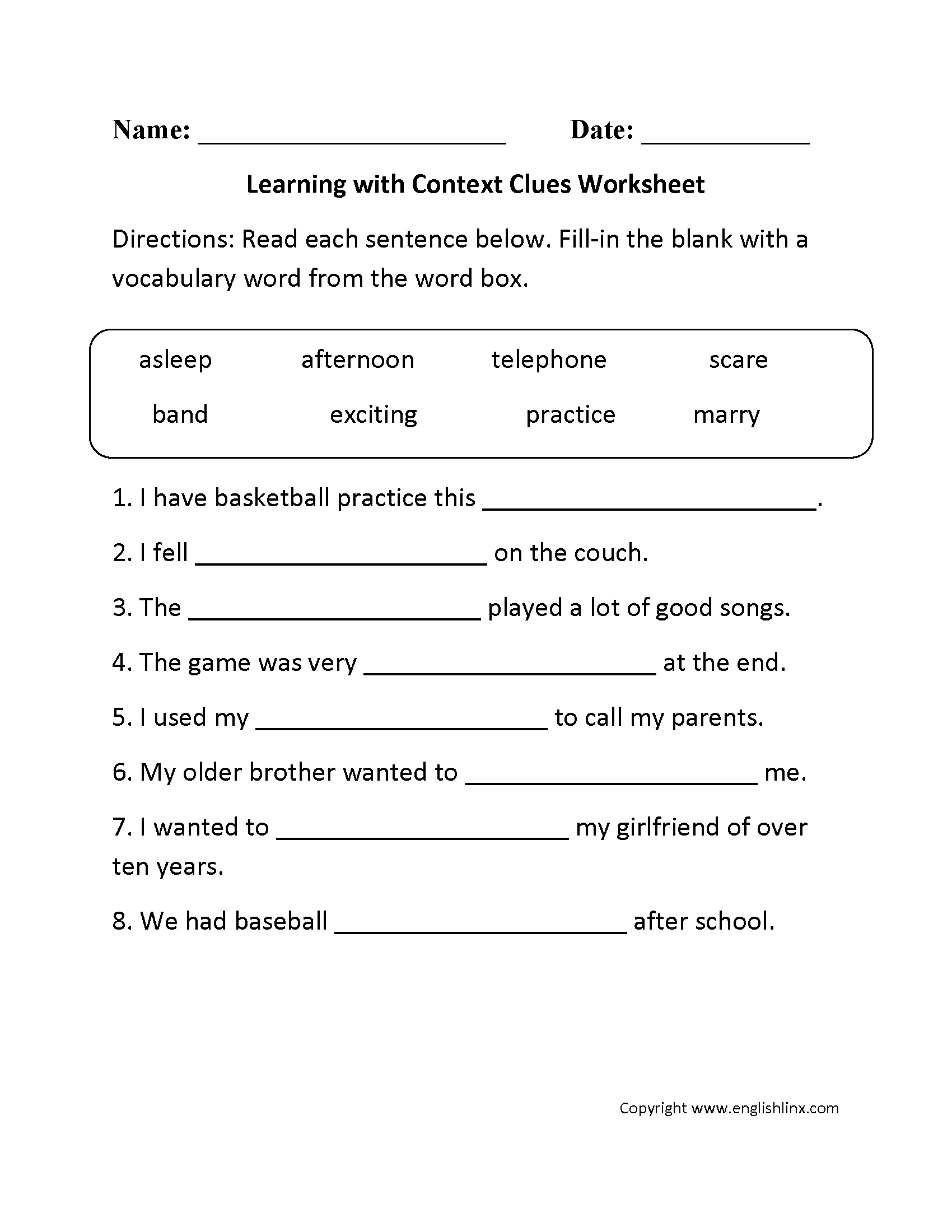
Worksheet Answer Key
- What is the main function of the ATP-ADP energy cycle? Answer: To generate and store energy for various cellular processes.
- What is the reaction that occurs during the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi? Answer: ATP → ADP + Pi
- What is the importance of the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP? Answer: To regenerate and store ATP for future energy needs.
- What is the role of inorganic phosphate (Pi) in the ATP-ADP energy cycle? Answer: Pi is released during energy release and used during energy storage.
What is the primary function of the ATP-ADP energy cycle?
+The primary function of the ATP-ADP energy cycle is to generate and store energy for various cellular processes.
What is the difference between ATP and ADP?
+ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is an energy-rich molecule that stores energy in the form of phosphate bonds, while ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is an energy-poor molecule that is converted to ATP during energy storage.
Why is the ATP-ADP energy cycle important for cellular functions?
+The ATP-ADP energy cycle is important for cellular functions because it allows for efficient energy transfer and storage, supporting various cellular processes such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and membrane transport.
In summary, the ATP-ADP energy cycle is a vital process that enables cells to generate and store energy for various cellular functions. Understanding the key players and stages of the cycle is essential for appreciating the importance of this process in maintaining cellular homeostasis.