Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers Simplified for Easy Learning
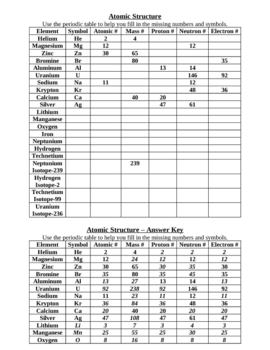
Understanding Atomic Structure: A Simplified Guide
Atomic structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the composition of atoms, which are the building blocks of matter. In this guide, we will break down the complex concept of atomic structure into simple, easy-to-understand sections.
What is Atomic Structure?
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement of electrons, protons, and neutrons within an atom. Atoms are the smallest units of a chemical element, and they are made up of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Protons
- Definition: Protons are positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus (center) of an atom.
- Charge: +1 (positive charge)
- Location: Nucleus (center) of the atom
- Function: Protons determine the chemical properties of an element and define its position in the periodic table.
Neutrons
- Definition: Neutrons are particles that have no charge and reside in the nucleus (center) of an atom.
- Charge: 0 (no charge)
- Location: Nucleus (center) of the atom
- Function: Neutrons help stabilize the nucleus and contribute to the atom’s mass.
Electrons
- Definition: Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus (center) of an atom.
- Charge: -1 (negative charge)
- Location: Orbitals (energy levels) around the nucleus
- Function: Electrons participate in chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of an element.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
- Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element’s identity and position in the periodic table.
- Mass Number (A): The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the atom’s mass.
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbitals (energy levels). Understanding electron configuration is crucial for predicting an element’s chemical properties and behavior.
- Electron Shells: Energy levels or orbitals that electrons occupy around the nucleus.
- Electron Subshells: Subdivisions of electron shells that contain specific numbers of electrons.
📝 Note: Electron configuration is a complex topic, and mastering it requires practice and patience.
Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
Here are the answers to common atomic structure worksheet questions:
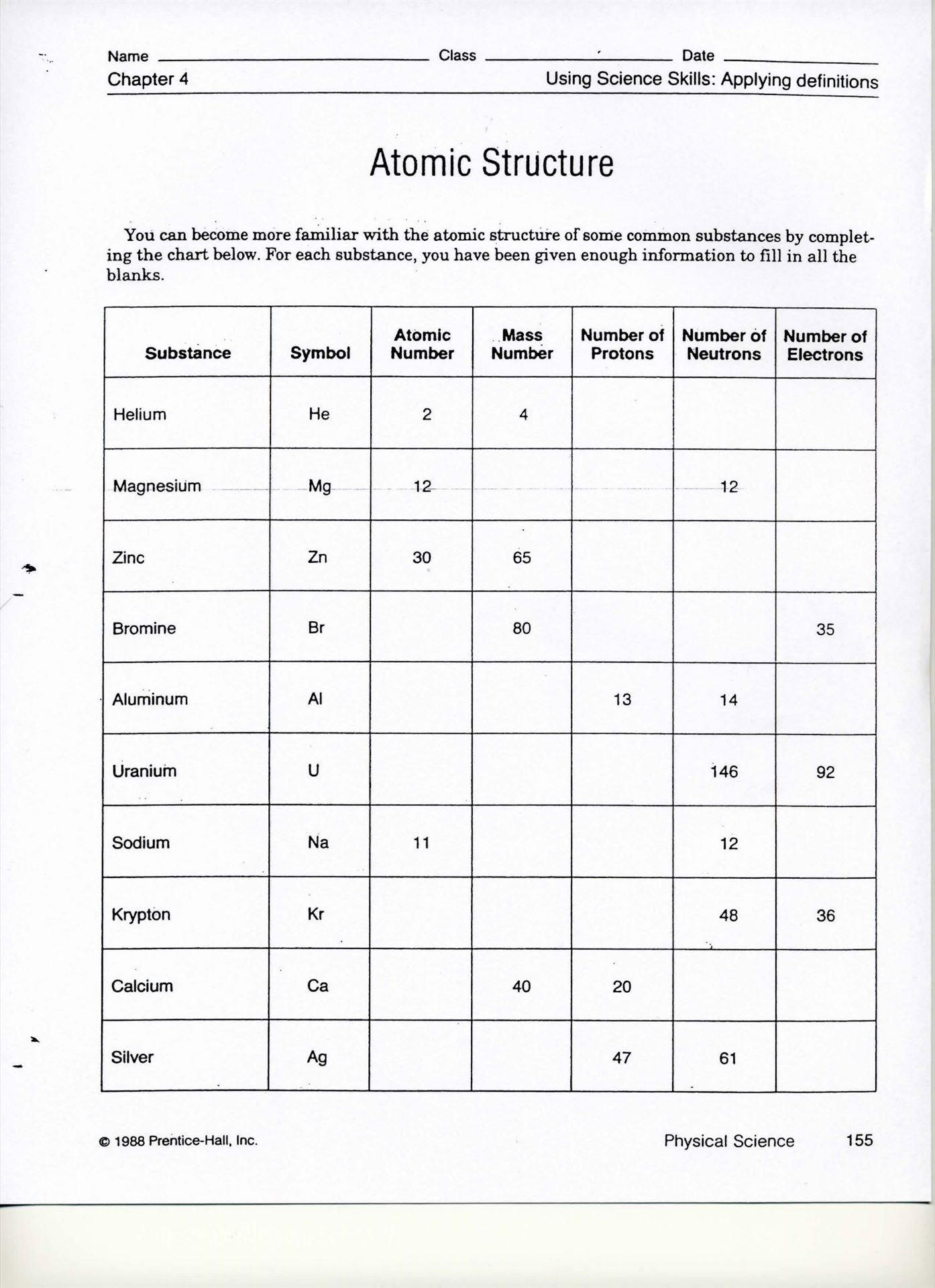
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the atomic number of an element? | The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. |
| What is the mass number of an element? | The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. |
| What is the function of protons in an atom? | Protons determine the chemical properties of an element and define its position in the periodic table. |
| What is the function of neutrons in an atom? | Neutrons help stabilize the nucleus and contribute to the atom’s mass. |
| What is the function of electrons in an atom? | Electrons participate in chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of an element. |
In conclusion, understanding atomic structure is essential for mastering chemistry. By grasping the concepts of protons, neutrons, electrons, atomic number, mass number, and electron configuration, you will be well on your way to becoming a chemistry whiz.
What is the difference between atomic number and mass number?
+
The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, while the mass number (A) is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
What is the function of electrons in an atom?
+
Electrons participate in chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of an element.
What is the definition of electron configuration?
+
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbitals (energy levels).
Related Terms:
- Atomic Structure Worksheet pdf