5 Ways to Master Food Webs and Food Chains
Understanding the Basics of Food Webs and Food Chains
Food webs and food chains are fundamental concepts in ecology that help us understand the relationships between different species in an ecosystem. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that eat other organisms as a source of food and energy, while a food web is a more complex network of food chains that show how different species are connected and interact with each other. Mastering food webs and food chains is essential for understanding the dynamics of ecosystems and the impact of human activities on the environment.
1. Learn the Key Components of Food Chains and Food Webs
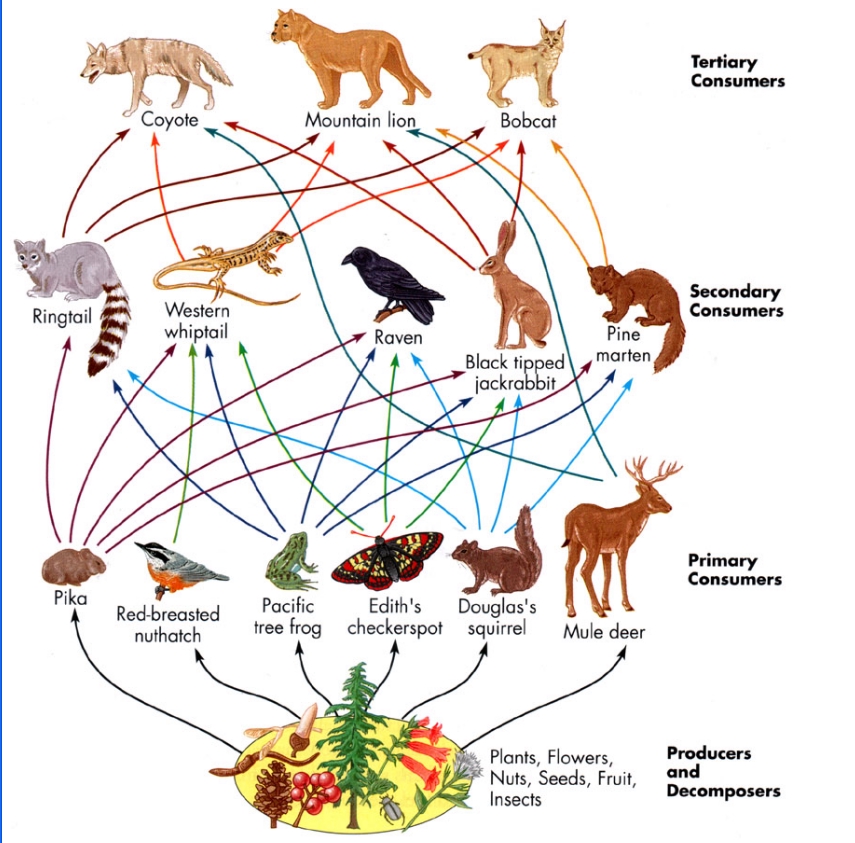
To master food webs and food chains, it’s essential to learn the key components that make them up. These include:
- Producers: organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants and algae.
- Consumers: organisms that eat other organisms as a source of food and energy, such as animals and insects.
- Decomposers: organisms that break down dead plants and animals into nutrient-rich soil, such as bacteria and fungi.
- Primary consumers: organisms that eat producers, such as herbivores.
- Secondary consumers: organisms that eat primary consumers, such as carnivores.
- Tertiary consumers: organisms that eat secondary consumers, such as apex predators.
2. Understand the Energy Flow in Food Chains and Food Webs
Energy flows through food chains and food webs from one organism to another. Producers convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, which is then transferred to consumers when they eat producers. The energy is then passed from one consumer to another, with each level of consumption losing some energy. This is known as the trophic cascade.
🌟 Note: The energy flow in food chains and food webs is often represented by a pyramid, with producers at the base and tertiary consumers at the top.
3. Identify the Types of Food Webs and Food Chains
There are several types of food webs and food chains, including:
- Grassland food web: a food web that consists of plants, herbivores, and carnivores in a grassland ecosystem.
- Marine food web: a food web that consists of phytoplankton, zooplankton, fish, and other marine animals.
- Freshwater food web: a food web that consists of aquatic plants, herbivorous fish, and carnivorous fish.
- Detrital food web: a food web that consists of decomposers, detritivores, and other organisms that feed on dead plants and animals.
4. Analyze the Impact of Human Activities on Food Webs and Food Chains
Human activities, such as overfishing, deforestation, and pollution, can have a significant impact on food webs and food chains. For example:
- Overfishing: can lead to the depletion of fish populations, which can have a cascading effect on the entire food web.
- Deforestation: can lead to the loss of habitat for many species, which can disrupt food chains and food webs.
- Pollution: can lead to the contamination of water and soil, which can affect the health of producers and consumers.
💡 Note: Understanding the impact of human activities on food webs and food chains is crucial for developing sustainable practices that conserve ecosystems.
5. Use Real-World Examples to Illustrate Food Webs and Food Chains
Using real-world examples can help illustrate the complex relationships between different species in an ecosystem. For example:
- The Serengeti ecosystem: a food web that consists of grasses, herbivores such as wildebeests and zebras, and carnivores such as lions and leopards.
- The coral reef ecosystem: a food web that consists of coral, algae, fish, and other marine animals.
By mastering food webs and food chains, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex relationships between different species in an ecosystem and the impact of human activities on the environment.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
+
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that eat other organisms as a source of food and energy, while a food web is a more complex network of food chains that show how different species are connected and interact with each other.
What are the key components of a food web?
+
The key components of a food web include producers, consumers, decomposers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers.
How do human activities impact food webs and food chains?
+
Human activities, such as overfishing, deforestation, and pollution, can have a significant impact on food webs and food chains, leading to the depletion of species populations and disrupting ecosystem balance.