5 Ways Amoeba Sisters Enzymes Worksheet Answers
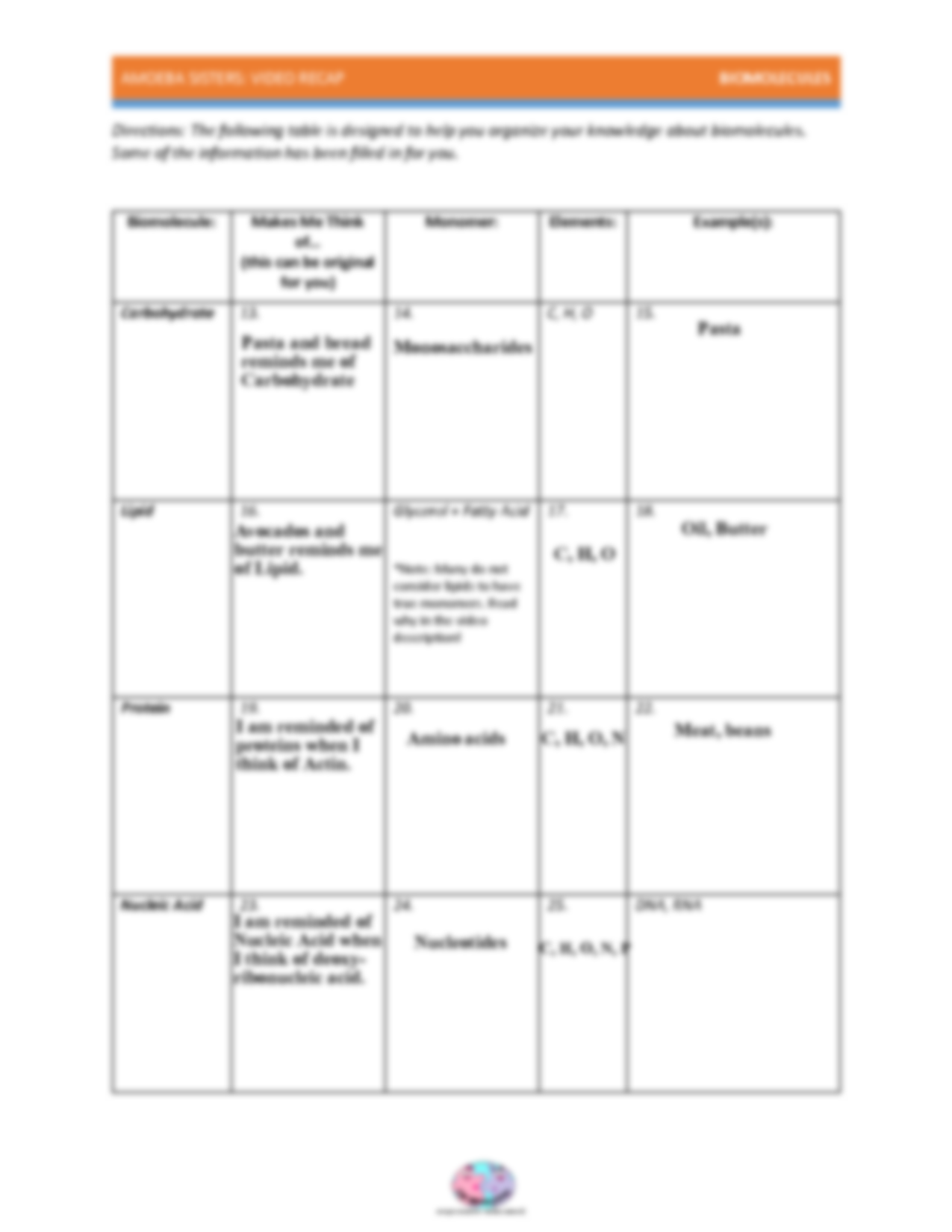
Understanding Enzymes with Amoeba Sisters
Enzymes play a crucial role in various biological processes, from digestion to DNA replication. The Amoeba Sisters, a popular educational YouTube channel, offer an engaging way to learn about enzymes through their animations and worksheets. In this article, we will explore five ways to use the Amoeba Sisters enzymes worksheet answers to enhance your understanding of enzymes.
What are Enzymes?
Before diving into the worksheet answers, let’s briefly review what enzymes are. Enzymes are biological molecules, typically proteins, that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. They act as catalysts, lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur, without being consumed in the process.
Amoeba Sisters Enzymes Worksheet Answers
The Amoeba Sisters offer a comprehensive worksheet on enzymes, covering topics such as enzyme structure, function, and regulation. Here are five ways to use the worksheet answers to improve your understanding of enzymes:
1. Enzyme Structure and Function
The worksheet answers explain that enzymes have an active site, which is the region that binds to the substrate (the molecule being acted upon). The shape and chemical properties of the active site determine the specificity of the enzyme.
- Key concept: Enzymes have a unique active site that allows them to bind to specific substrates.
- Example: Trypsin, a digestive enzyme, has an active site that binds to peptides with a specific amino acid sequence.
2. Types of Enzymes
The worksheet answers categorize enzymes into six main classes:
Oxidoreductases (e.g., catalase)
Transferases (e.g., kinases)
Hydrolases (e.g., amylase)
Lyases (e.g., lactate dehydrogenase)
Isomerases (e.g., glucose isomerase)
Ligases (e.g., DNA ligase)
Key concept: Enzymes can be classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze.
Example: Amylase is a hydrolase that breaks down starch into simple sugars.
3. Enzyme Regulation
The worksheet answers discuss various ways enzymes can be regulated, including:
Allosteric control (binding of regulatory molecules to non-active sites)
Competitive inhibition (binding of inhibitor molecules to the active site)
Non-competitive inhibition (binding of inhibitor molecules to other sites on the enzyme)
Key concept: Enzymes can be regulated through various mechanisms to control their activity.
Example: Allosteric control allows enzymes to be activated or inhibited in response to changes in substrate concentration.
4. Enzyme Denaturation
The worksheet answers explain that enzymes can be denatured by changes in temperature, pH, or solvent composition. Denaturation disrupts the enzyme’s native conformation, rendering it inactive.
- Key concept: Enzymes are sensitive to changes in their environment, which can affect their activity.
- Example: Heat denaturation can inactivate enzymes, such as trypsin, by disrupting their native conformation.
5. Medical Applications of Enzymes
The worksheet answers highlight the importance of enzymes in medical applications, such as:
Enzyme replacement therapy (e.g., for genetic disorders like phenylketonuria)
Enzyme inhibition (e.g., for diseases like hypertension or cancer)
Key concept: Enzymes play a crucial role in medical applications, from diagnosis to treatment.
Example: Enzyme replacement therapy can help manage genetic disorders by supplementing deficient enzymes.
💡 Note: The Amoeba Sisters enzymes worksheet answers provide a comprehensive review of enzyme biology. By understanding these concepts, you can better appreciate the importance of enzymes in various biological processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Amoeba Sisters enzymes worksheet answers offer a valuable resource for learning about enzymes. By exploring the structure, function, regulation, denaturation, and medical applications of enzymes, you can gain a deeper understanding of these biological molecules. Remember to use the worksheet answers as a starting point for further exploration and learning.
What is the primary function of enzymes?
+Enzymes act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in living organisms without being consumed in the process.
What is the difference between competitive and non-competitive inhibition?
+Competitive inhibition involves the binding of inhibitor molecules to the active site, whereas non-competitive inhibition involves the binding of inhibitor molecules to other sites on the enzyme.
How do enzymes contribute to medical applications?
+Enzymes play a crucial role in medical applications, such as enzyme replacement therapy and enzyme inhibition, which can help manage genetic disorders and diseases.
Related Terms:
- Amoeba Sisters Enzymes Worksheet PDF
- Amoeba Sisters worksheets
- Amoeba Sisters video recap answers
- Enzyme substrate and active site
- Lactase and lactose enzyme illustration
- Illustrate an enzyme and substrate