5 Ways to Master Acceleration Calculations
Understanding Acceleration and Its Importance in Physics
Acceleration is a fundamental concept in physics that measures the rate of change of velocity. It is a crucial aspect of motion, as it helps us understand how objects move and respond to forces. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. In simpler terms, it is the measure of how quickly an object’s velocity changes. Mastering acceleration calculations is essential for anyone studying physics, engineering, or mathematics.
1. Learn the Basics: Understanding Acceleration Formulas
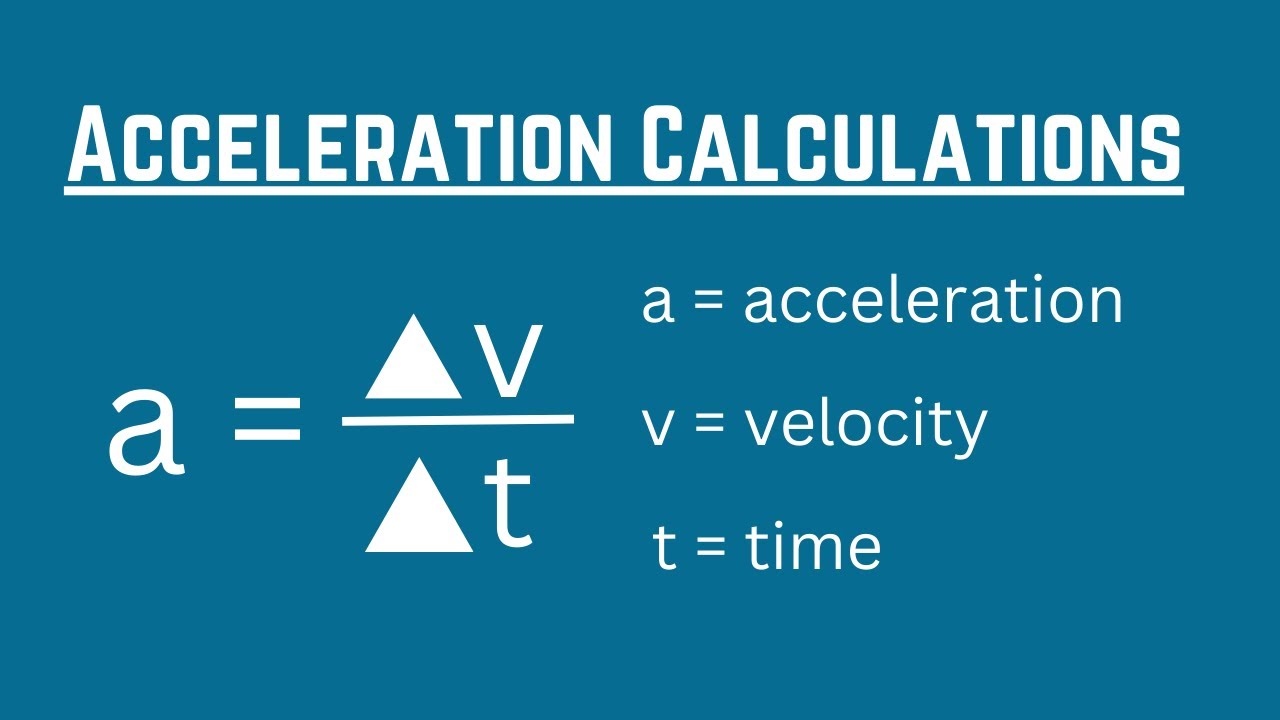
To master acceleration calculations, you need to understand the basic formulas and equations involved. The most commonly used formula for acceleration is:
a = Δv / Δt
where:
- a is the acceleration
- Δv is the change in velocity
- Δt is the time interval over which the acceleration occurs
Another essential formula is:
a = v / t
where:
- a is the acceleration
- v is the final velocity
- t is the time
Understanding these formulas will help you solve a wide range of acceleration problems.
2. Practice with Simple Problems: Building Your Foundation
Practice makes perfect, and acceleration calculations are no exception. Start by solving simple problems, such as:
- An object moves from rest to a velocity of 20 m/s in 4 seconds. What is its acceleration?
- A car accelerates from 0 to 60 km/h in 10 seconds. What is its acceleration?
Use the formulas above to solve these problems, and gradually move on to more complex ones.
3. Visualize the Motion: Graphical Analysis
Graphical analysis is a powerful tool for understanding acceleration. By plotting velocity against time, you can visualize the motion and calculate acceleration. Use graphs to:
- Identify the initial and final velocities
- Determine the time interval
- Calculate the acceleration
Graphical analysis will help you develop a deeper understanding of acceleration and how it relates to velocity and time.
4. Apply Acceleration to Real-World Problems: Case Studies
Acceleration has numerous real-world applications, from designing roller coasters to optimizing traffic flow. Use case studies to apply acceleration calculations to practical problems, such as:
- A roller coaster car accelerates from rest to 90 km/h in 10 seconds. What is its acceleration?
- A motorcycle accelerates from 0 to 100 km/h in 5 seconds. What is its acceleration?
By applying acceleration calculations to real-world problems, you will develop a more nuanced understanding of the concept.
5. Review and Refine: Common Mistakes and Best Practices
Reviewing and refining your acceleration calculations is crucial to mastering the concept. Common mistakes include:
- Forgetting to convert units
- Using the wrong formula
- Neglecting to consider initial velocity
Best practices include:
- Always labeling your diagrams and graphs
- Checking your units and conversions
- Breaking down complex problems into simpler ones
By reviewing and refining your acceleration calculations, you will become more confident and proficient in your ability to solve problems.
🤔 Note: Acceleration calculations can be complex and require attention to detail. Make sure to double-check your work and use multiple methods to verify your answers.
To summarize, mastering acceleration calculations requires a combination of understanding the basics, practicing with simple problems, visualizing the motion, applying acceleration to real-world problems, and reviewing and refining your work. By following these steps and using the formulas and techniques outlined above, you will become proficient in acceleration calculations and develop a deeper understanding of motion and physics.
What is the difference between velocity and acceleration?
+Velocity is the rate of change of an object’s position, while acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. In other words, velocity describes an object’s speed and direction, while acceleration describes how quickly that velocity changes.
Can acceleration be negative?
+Yes, acceleration can be negative. When an object’s velocity decreases, its acceleration is negative. For example, when a car slows down, its acceleration is negative.
What is the unit of acceleration?
+The unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s^2) or kilometers per hour squared (km/h^2).